Briefly Explain Different Keys in Database With Examples
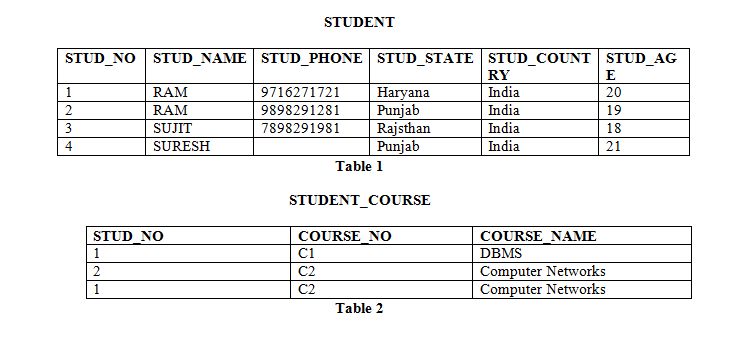
For Example STUD_NO COURSE_NO is a composite candidate key for relation STUDENT_COURSE. In other words the foreign key forces a table to be linked to the data of another table.
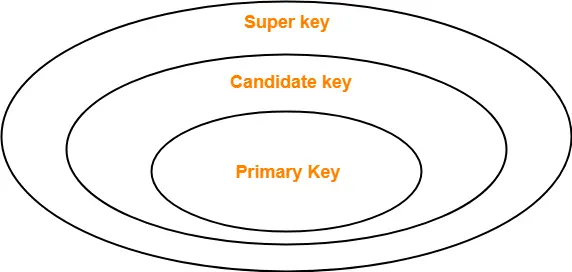
It is a set of attributes that uniquely identifies a row.
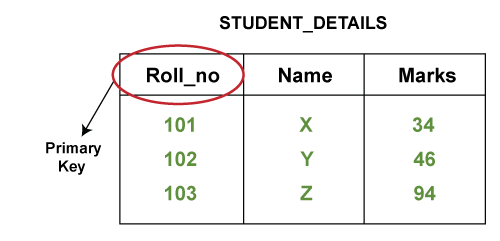
. Primary Key - The primary key is selected from one of the candidate keys and becomes the identifying key of a table. If you have any problem in these database keys then please comment below. The students unique student ID number is a good choice for a primary key in the STUDENTS table.
Lets look at each of them separately. Here you can have a secondary index in DBMS for every search-key. Alternate key can also work as a primary key.
Example of Foreign Key. Types of Keys in DBMS. It must also have atomicity ie.
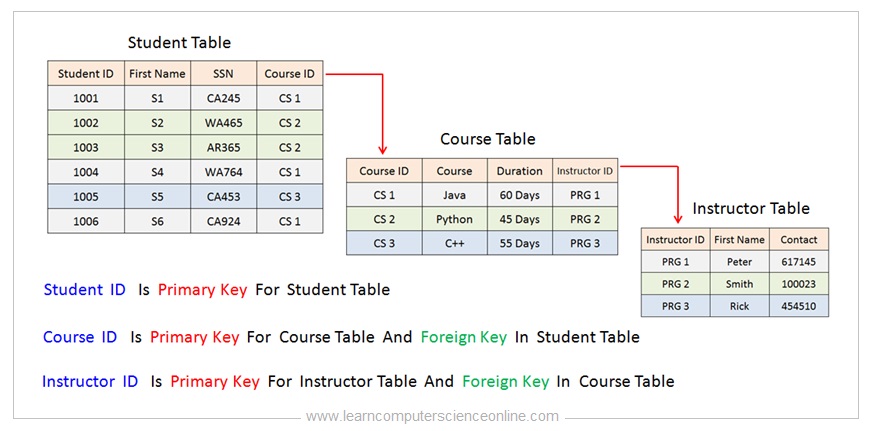
Primary Key in Student_Information Table. So all these are the Various Keys in Database Management System DBMS. Social Security Number SSN is a natural key that can be declared as the primary key.
Objectives Explain the physical. Define user views and explain their function. Several techniques have been proposed for the distribution of public keys.
Candidate Key - The candidate keys in a table are defined as the set of keys that is minimal and can uniquely identify any data row in the table. A primary key is one of the Candidate Keys. It can be divided into smaller sub parts each sub part can form an independent attribute.
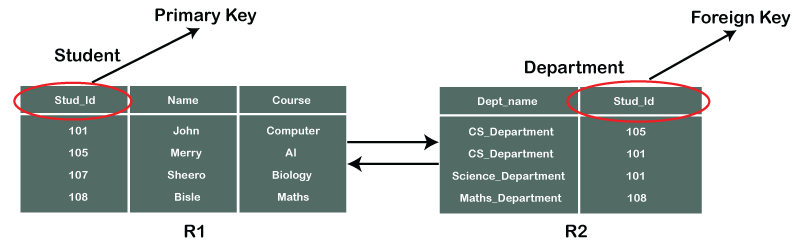
There may be more than candidate key and may be a combination of more than one attribute. Alternate key is also called Secondary Key. In the following example Orders table is linked to Persons table by PersonID.
These types of databases are also sometimes referred to as non-relational databases. Sample of key attribute. Briefly explain with example how key distribution can be achieved.
What are the different steps involved in the public key authority key distribution. The above-mentioned anomalies occur because inadvertently we are storing two or more pieces of information in every row of a table. For the table in Img1 if the manager MrXs name has to be updated the update operation must be applied to all the rows that MrX is associated withMissing out even a single row causes inconsistency of data within the database.
Lets understand secondary indexing with a database index example. For example a table of customer orders might have a user column with a foreign key. You may want to find all accounts in of a specific branch of ABC bank.
Database systems like any other computer system are subject to failures but the data stored in it must be available as and when requiredWhen a database fails it must possess the facilities for fast recovery. Alternate Key in Branch_Info table. The candidate key can be simple having only one attribute or composite as well.
What is a relational database exactly. Primary Key in Branch_Info table. The most common and frequently used example of the surrogate key is the auto generated integer values in the increasing sequential order such as 1 2 3 4 5.
Microsoft SQL Server Oracle Database MySQL PostgreSQL and IBM Db2. Name FirstName MiddelName LastName. RABCDE then total no of candidate keys are 5Cfloor5210.
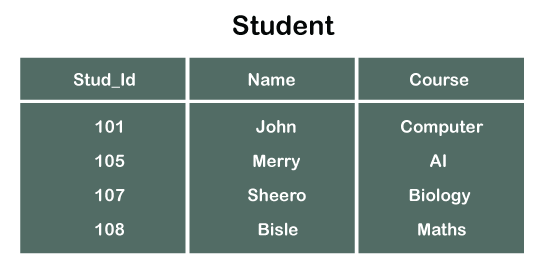
It can uniquely identify any data row of the table. The different types of keys in DBMS are. The students first and last name are not good choices because there is always the chance that more than one student might have the same name.
On the contrary A surrogate key is not a natural key because surrogate key attribute is specifically added to the table as a prime attribute for the purpose of defining the primary key. Imagine you have a STUDENTS table that contains a record for each student at a university. This attribute represents the main characteristic of an entity ie.
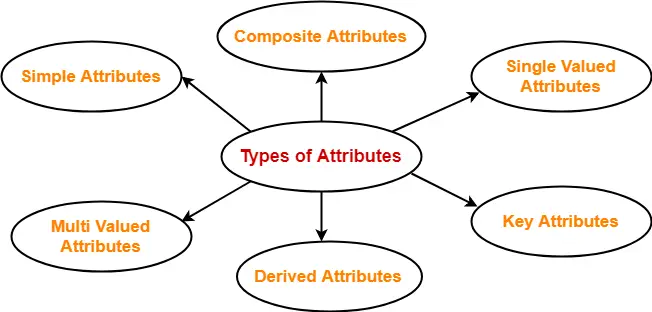
The different types of attributes are as follows. Examples of Database Management System. Present a methodology for database design at the information level and view examples illustrating.
Index record is a record point to a bucket that contains pointers to all the records with their. The attributes of student entity are as follows. While we must admit their popularity is growing the relational databases still take up the lions share of the market.
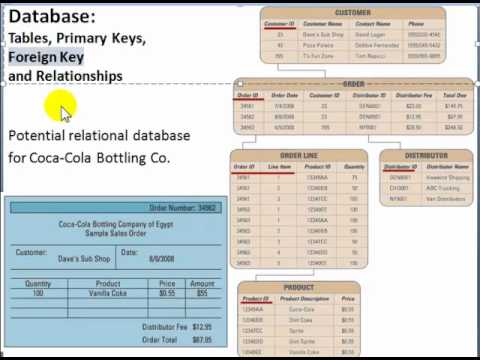
A primary key is a column of a table or a set of columns that helps to identify every record present in that table uniquely. A foreign key is a simple mechanism to ensure referential integrity between data in different tables. In a bank account database data is stored sequentially by acc_no.
Explain Database Scheme and Its types. It is a set of one or more attributes that can uniquely identify tuples in a relation. Alternate keys are candidate keys that are not selected as primary key.
Primary Key Example. Key attribute has clearly different value for each element in an entity set. No of candidate keys in a Relation are nCfloorn2for example if a Relation have 5 attributes ie.
A few simple non-relational database examples would be key-value stores document stores or graph databases. Suppose you are given the following requirements for a simple database for the football. NoSQL is a broad category that includes any database that doesnt use SQL as its primary data access language.
The entity student ID is a key attribute because no other student will have the same ID. Either transactions are completed successfully and committed the effect is recorded permanently in the database or the. Create an entity-relationship diagram to visually represent a database design.
On a technical level a foreign key is a constraint that links a column in one table table_1column_a to a column in a different table table_2column_b and ensures that a value can be added to column_a only if the same value already exists in column_b. The first to mention the term relational database was Edgar F. Define database design language and use it to document database designs.
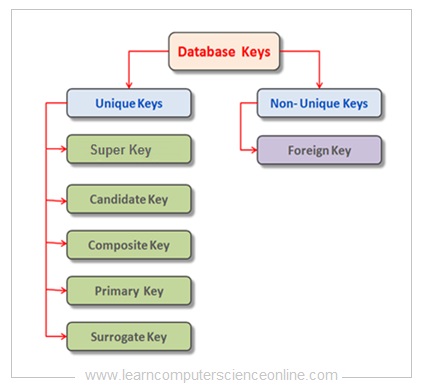
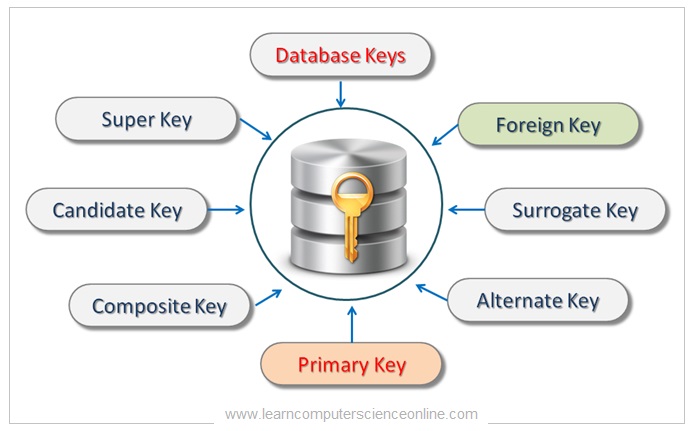
There are broadly seven types of keys in DBMS.
Database Keys Explained Primary Key Foreign Key Key Types In Dbms

Different Types Of Keys In Dbms Webeduclick
Foreign Key In Dbms Javatpoint
Primary Key In Dbms Javatpoint
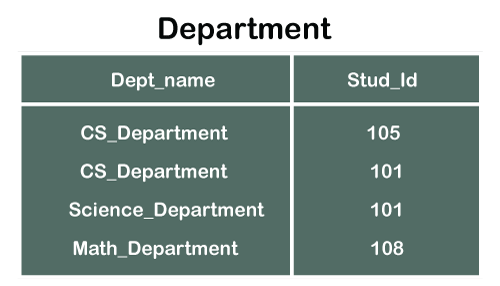
Foreign Key In Dbms Javatpoint
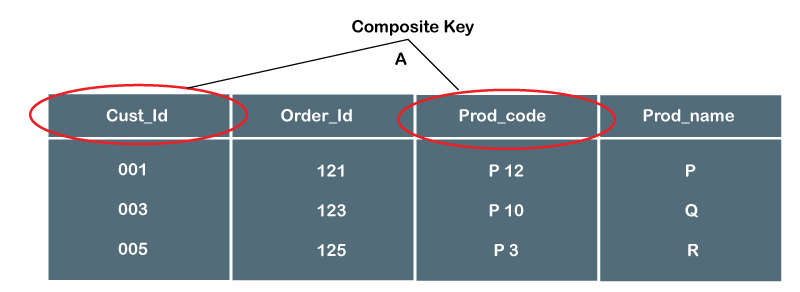
Composite Key In Dbms Javatpoint
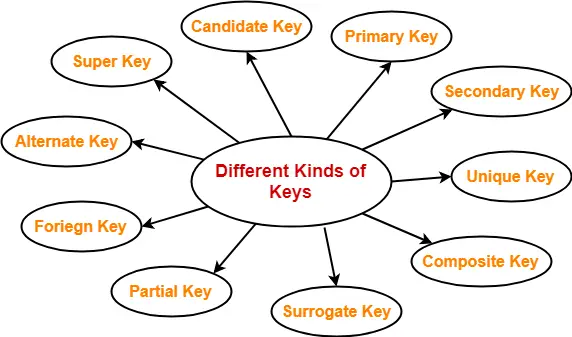
Types Of Keys In Dbms Definitions Examples Gate Vidyalay
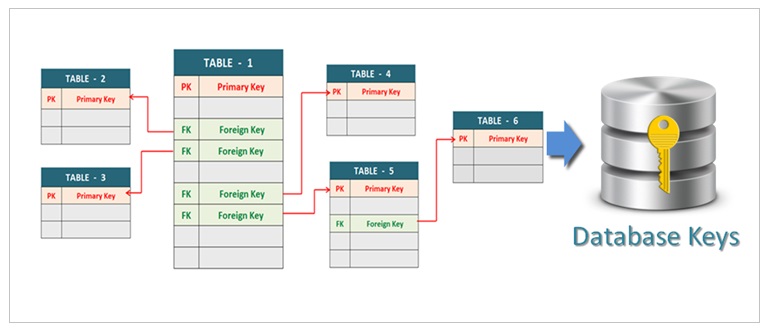
Database Keys Explained Primary Key Foreign Key Key Types In Dbms
Types Of Keys In Dbms Definitions Examples Gate Vidyalay

What Is Database Its Types And Examples Examplanning
Database Keys Explained Primary Key Foreign Key Key Types In Dbms
Difference Between Primary Key And Foreign Key Geeksforgeeks
Database Keys Explained Primary Key Foreign Key Key Types In Dbms
Types Of Attributes Dbms Gate Vidyalay

7 Different Types Of Database Keys Explained With Example
Database Tables Primary Keys Foreign Keys And Relationships Youtube


Comments
Post a Comment